Seismic drift demand estimation for steel moment frame buildings: from mechanics-based to data-driven models
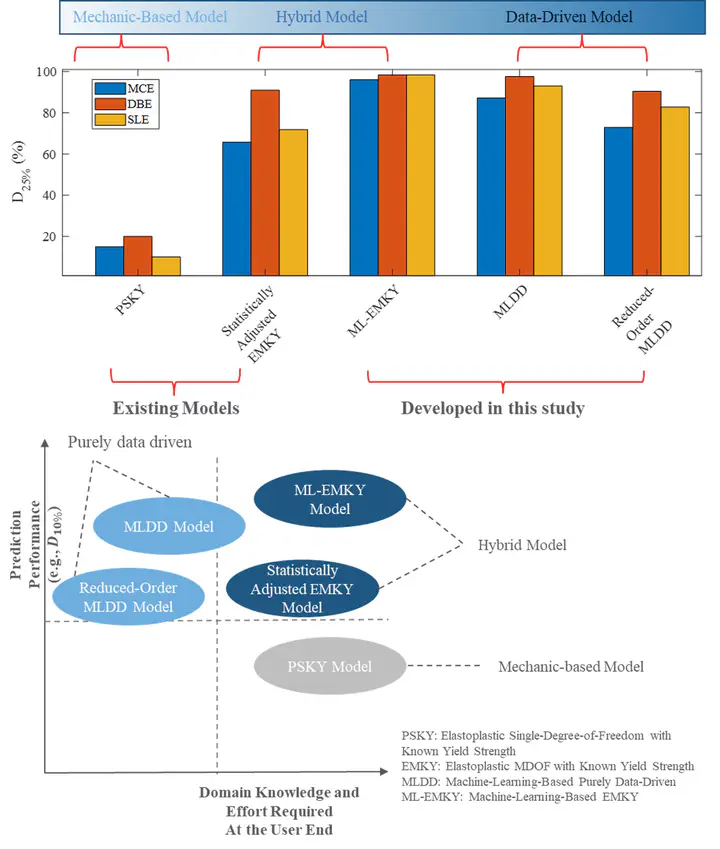 Comparative Assessment Among Different Models
Comparative Assessment Among Different Models
Abstract
A spectrum of simplified methods for estimating building seismic drift demands is conceptualized. On one extreme are mechanics-based approaches that are derived solely from fundamental engineering principles. On the other end are purely data-driven models that are developed using parametric data sets generated from nonlinear response history analyses. Between these two extremes, there are models that combine elements of basic engineering principles and statistical learning (hybrid models). First, the benefits and drawbacks of four existing simplified seismic response estimation methodologies that fall within this spectrum of approaches are critically examined. Subsequently, a generalized framework for developing and validating hybrid and/or purely data-driven seismic demand estimation models is proposed. Using this framework, two new machine learning–based models are developed and rigorously evaluated. Finally, a comparative assessment of the existing and newly developed models is conducted while focusing on their predictive performance and the level of effort needed to implement them.